Health-GPS

Global Health Policy Simulation model
Global Health Policy Simulation model
| Home | Quick Start | User Guide | Software Architecture | Data Model | Developer Guide | API |
Data Model
The backend data model defines an abstract model to organises data entities and how they relate to one another in a standardised schema and format to be used within the Health-GPS systems. The backend storage provides a reference dataset that reconcile various disparate data sources required by the model, fill gaps, adjust units, etc, for easy use. The standardised format allows the reference dataset to be easily expanded to accommodate new and non-traditional data sources.
The data model is storage agnostic, the Data API abstraction interface shown below, provides a contract for the minimum dataset, easy access, strong typing, and decoupling from the backend storage implementation.
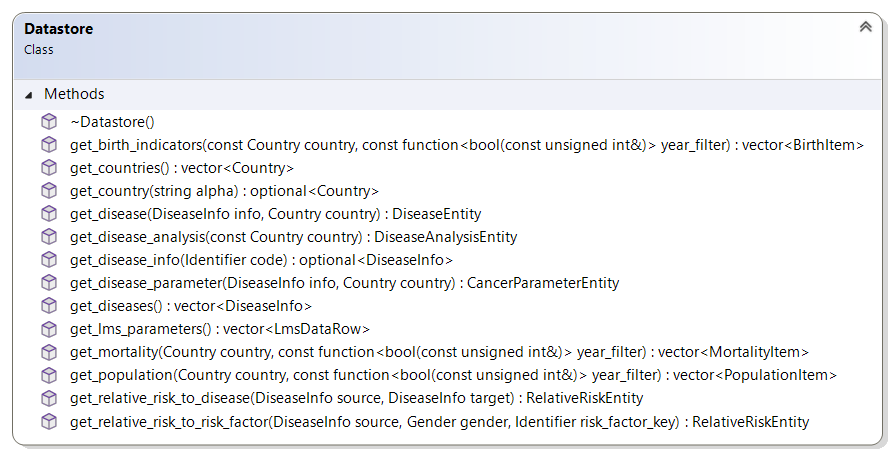 |
|---|
| Backend Data API Interface |
The data model defines the minimum dataset required by the model, the backend storage can hold more data to support external analysis for example. The backend dataset diagram is shown below, it identifies the required entities, relationships, and fields with respective data types. The dataset is indexed by country, green, entities representing demographics are gray, diseases are red, analysis are blue, and enumeration types are yellow respectively. Primary key (PK) fields are shown in bold, the ID fields are auto-generated row identifiers for internal use and data integrity enforcement.
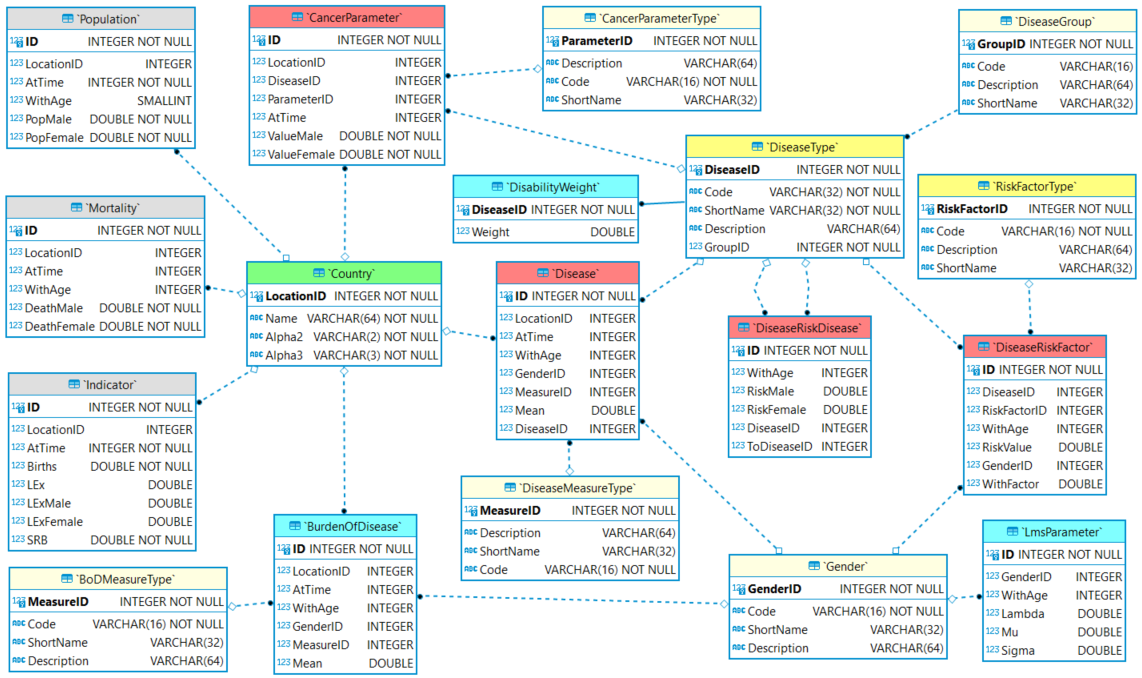 |
|---|
| Data Model Entity–Relationship Diagram |
The country index entity is based on the ISO 3166-1 standard. All external data sources must provide some kind of location identifier, most likely with different values, but must enable mapping with the data storage index definition to be reconcile.
Enumerations
The data model defines normalised enumerations, yellow, to provide stable identifier for the commonly used concepts, such as gender, and consistent dimensional data lookups. Enumerations are defined by four fields as shown below, must populated before any data entry, provide also mapping with external data sources during the reconcile process.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| XyzID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| Code | Text | UQ | User stable identifier |
| ShortName | Text | User facing display name | |
| Description | Text | Optional documentation |
The unique constraint (UQ) may include multiple fields within the entity definition, ShortName fields are the user facing name for the code identifier and must always be provided. It is very important to be consistent when populating the enumerations code field to provide users and applications stable lookups, the following list is a suggested guide:
- start with a letter
- use only letters, numbers, and/or the underscore character, no spaces
- be consistent with casing, prefer lower case, avoid mixing
- keep it short, but meaningful and recognisable
The same recommendation applies to folders and file names definitions in cross-platform applications, operating system like Linux is case-sensitive by default, adopt a consistent naming convention that works everywhere. Following are enumerations defined by the Health-GPS model:
Gender
| GenderID | Code | ShortName | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | male | Male | |
| 2 | female | Female |
Disease Group
| GroupID | Code | ShortName | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | other | Other | General noncommunicable diseases |
| 1 | cancer | Cancer | Cancer type diseases |
Disease Measure Type
| MeasureID | Code | ShortName | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | prevalence | Prevalence | ||
| 6 | incidence | Incidence | ||
| 7 | remission | Remission | ||
| 15 | mortality | Mortality |
BoD Measure Type
| MeasureID | Code | ShortName | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | daly | DALY | Disability adjusted life years |
| 3 | yld | YLD | Years lived with disability |
| 4 | yll | YLL | Years of life lost |
Cancer Parameter Type
| ParameterID | Code | ShortName | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | deathweight | Deaths | Death weight |
| 1 | prevalence | Prevalence | Prevalence distribution |
| 2 | survivalrate | Survival | Survival rate parameters |
Registries
The DiseaseType and RiskFactorType are dynamic enumerations, providing a consistent Registry for available diseases and relative risk factors respectively. These enumerations are populated on demand, when defining new diseases within the Health-GPS ecosystem. Following are the examples of dynamic enumerations defined in the Health-GPS model:
Disease Type
| DiseaseID | Code | GroupID | ShortName | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auto | asthma | 0 | Asthma | |
| Auto | diabetes | 0 | Diabetes | Diabetes mellitus type 2 |
| Auto | lowbackpain | 0 | Low back pain | |
| Auto | colorectum | 1 | Colorectal cancer |
Risk Factor Type
| ParameterID | Code | ShortName | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto | bmi | BMI | Body Mass Index |
The risk factor code must be consistent, and exact match the risk factor naming convention used in the external model’s definition. Only risk factors with relative effects on diseases data should be registered to minimise the constraint on external modelling.
Data Entities
All entities in the model have a time and/or age dimension associated with the measures being stored. The following notation is used to represent these two dimensions across the data model:
| Field Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AtTime | Integer | The time reference in years |
| WithAge | Integer | Time reference at time in years |
Entities with a single measure associated with gender, e.g. Population, store the values for each enumeration as column, while entities with higher dimensionality, e.g. disease, represent Gender and Measure independent dimensions. All data stored in the model should have a consistent unit, with all unit’s conversion performed outside prior to data ingestion.
Demographics
Country specific demographics data containing historic estimates and projections are modelled using one entity per measure, representing a two-dimensional series, time x age, with expanded gender enumeration columns. The following entities provide the demographics module data, all fields are required for a row definition.
Population
Stores the number of males and females measure for a location at each time and age combination.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| LocationID | Integer | UQ | Location unique identifier |
| AtTime | Integer | UQ | Time reference of the measure values |
| WithAge | Integer | UQ | Age reference of the measure values |
| PopMale | Real | Number of males in population | |
| PopFemale | Real | Number of female in population |
Mortality
Stores the number for male and female deaths for a location at each time and age combination.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| LocationID | Integer | UQ | Location unique identifier |
| AtTime | Integer | UQ | Time reference of the measure values |
| WithAge | Integer | UQ | Age reference of the measure values |
| DeathMale | Real | Number of males deaths in population | |
| DeathFemale | Real | Number of female deaths in population |
Indicators
Stores general population indicators number for a location at each time entry.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| LocationID | Integer | UQ | Location unique identifier |
| AtTime | Integer | UQ | Time reference of the indicator values |
| Births | Real | Number of births, both sexes combined | |
| SRB | Real | Sex ratio at birth (male births per female births) | |
| LEx | Real | Life expectancy at birth for both sexes combined in years | |
| LExMale | Real | Male life expectancy at birth (years) | |
| LExFemale | Real | Female life expectancy at birth (years) |
Diseases
Countries disease specific estimates are modelled using a multi-dimensional entity to represent a two dimensional series, time x age, for gender and measure type combinations. The following entities provide the diseases model required data, all fields are required for a row definition.
Disease
Diseases can be dynamic defined within the Health-GPS framework using data only. The disease entity models the common measures required to define all diseases.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| LocationID | Integer | UQ | Location unique identifier |
| DiseaseID | Integer | UQ | Disease type unique identifier |
| MeasureID | Integer | UQ | Measure type unique identifier |
| GenderID | Integer | UQ | Gender type unique identifier |
| AtTime | Integer | UQ | Time reference of the measure values |
| WithAge | Integer | UQ | Age reference of the measure values |
| Mean | Real | The measure mean value |
Cancer Parameter
In addition to the common data above, cancers definition requires extra parameters, which are modelled using a multi-dimensional entity, storing time-based parameter values using expanded gender enumeration as columns.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| LocationID | Integer | UQ | Location unique identifier |
| DiseaseID | Integer | UQ | Disease type unique identifier |
| ParameterID | Integer | UQ | Parameter type unique identifier |
| AtTime | Integer | UQ | Time reference of the measure values |
| ValueMale | Real | The parameter value for males | |
| ValueFemale | Real | The parameter value for females |
Relative Risks
The disease relative risk measure represents the association of risk factors and diseases, how exposures to risk factors affects the probabilities of developing the disease, the incidence of diseases in the population.
Relative risk to Disease (DiseaseRiskDisease)
The diseases relative risk to other diseases is modelled to represent the relative risk values by age using expanded gender enumeration as columns.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| DiseaseID | Integer | UQ | Disease type unique identifier |
| ToDiseaseID | Integer | UQ | Relative to disease type unique identifier |
| WithAge | Integer | UQ | Age reference of the risk values |
| RiskMale | Real | The relative risk value for males | |
| RiskFemale | Real | The relative risk value for females |
Relative Risk due to Risk Factor (DiseaseRiskFactor)
The risk factors relative risk to diseases is modelled as a two-dimensional entity with age x factor value lookups value, stored for the relevant diseases by gender.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| DiseaseID | Integer | UQ | Disease type unique identifier |
| RiskFactorID | Integer | UQ | Relative to risk factor unique identifier |
| GenderID | Integer | UQ | Gender type unique identifier |
| WithAge | Integer | UQ | Age reference of the risk values |
| WithFactor | Real | UQ | Factor reference of the risk values |
| RiskValue | Real | The relative risk values |
Analysis
Defines the data model to support the analysis modules, which calculates among other things calculates the Burden of Diseases (BoD) indicators, describing death and loss of health due to diseases, injuries, and risk factors for the simulated population.
Disability Weight
Stores disease specific disability weight estimates, which representing the magnitude of health loss associated with specific health outcomes, used to calculate years lived with disability (YLD) for these outcomes in a given population.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DiseaseID | Integer | PK | Disease type unique identifier |
| Weight | Real | The disease weight value |
LMS Parameters
Stores the Lambda-Mu-Sigma (LMS) model parameters, which is used to convert BMI risk factor values to z-scores for children.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Parameter unique identifier |
| GenderID | Integer | UQ | Gender type unique |
| WithAge | Integer | UQ | Age reference of the parameter |
| Lambda | Real | The lambda parameter value | |
| Mu | Real | The mu parameter value | |
| Sigma | Real | The sigma parameter value |
Burden of Disease
The burden of diseases (BoD) measure is modelled using a two-dimensional entity, time x age, to represent the measure values for each gender enumeration entry.
| Field name | Data Type | Constraint | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Integer | PK | Model unique identifier |
| LocationID | Integer | UQ | Location unique identifier |
| MeasureID | Integer | UQ | BoD measure type unique identifier |
| GenderID | Integer | UQ | Gender type unique identifier |
| AtTime | Integer | UQ | Time reference of the measure values |
| WithAge | Integer | UQ | Age reference of the measure values |
| Mean | Real | The measure mean value |
The data model definition is now complete. The design makes heavy use of relational-database notations; however, the backend data model is storage and implementation agnostic, the Health-GPS ecosystem seamlessly supports different Data API implementations via instance injection during construction.
See Development Guide for a file-based backend storage implementation detail.